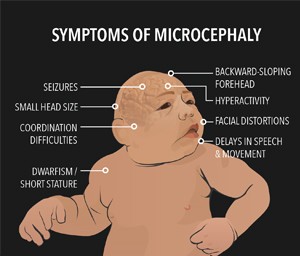
Zika virus therefore remains a major concern, especially to pregnant women given its relationship with congenital Zika syndrome (CZS), with children displaying defects such as microcephaly at their birth. The facts discussed in this article include the ways of getting infected, the signs of the disease, prevention, and global management stressing on the severity of raising awareness and effective management of mosquitoes in affected areas.

Introduction:
Apart from the chikungunya infection, the Zika virus, which is a type of flavivirus transmitted by the mosquito, went viral in the South America region in 2015-2016. This led to a lot of worry owing to the link it had with major congenital malformations such as microcephaly and other neurological abnormalities. This article aims at discussing the current state of research with regard to Zika virus and vaccines and therapies under development for the virus.
Understanding Zika Virus
Transmission and Symptoms
The disease is mainly spread by the Aedes species of mosquitoes that are infected with the virus. Sexual contact, contaminated blood and its products, and from an infected mother to her fetus during pregnancy. The symptoms of the disease are usually flu-like with high fever, rash, joint pain, and conjunctivitis that may persist for a few days to one week. However, most patients who contracts this disease will not realize it because they will have no symptoms at all.
Complications
The main reason people worry about Zika virus infection is its connection to congenital Zika syndrome that results in a child’s microcephaly, brain damage, etc. Moreover, the pregnant women getting infected with Zika can develop Guillain-Barré syndrome which is a severe neurological disorder marked by paralysis.
Vaccine Development
Traditional Vaccine Approaches
Several traditional vaccine platforms are being explored for Zika virus.
1. Inactivated Virus Vaccines: These vaccines use killed versions of the virus to induce an immune response. Animal tests have been carried out with relative success in eliciting protective immunity without the occurrence of disease.
2. Live Attenuated Vaccines: These vaccines have a live virus which has been attenuated, as a way of provoking the human body’s immune response. It has been found to be useful in animal models, but studies have not provided sufficient evidence about its safety for pregnant women.
3. Protein Subunit Vaccines: These vaccines use viral proteins to trigger an immune response. While the current vaccination uses the whole virus as the active component, ongoing research aims to determine the best viral components to use in the vaccines.
Innovative Vaccine Strategies
Researchers are also exploring innovative approaches to Zika virus vaccination.
1. mRNA Vaccines: Building on the experience and success of using mRNA to develop vaccines against COVID-19, there are several vaccine candidates for Zika virus. These vaccines introduce pieces of the virus into the body and the body itself must come up with an immune response to it. Well-tolerated, and with encouraging preclinical findings, trials are currently being conducted.
2. DNA Vaccines: DNA vaccines involves the use of plasmids which contain genetic information that is needed to produce antigens which are viral in nature and will elicit a response on the body. These comprise the initial clinical studies, which have shown the safety of this approach, as well as its immunogenicity, thus rendering the approach feasible for vaccination against Zika virus.
3. Viral Vector Vaccines: These vaccines involve the use of related viruses that are harmless but are engineered to introduce Zika virus genes into cells to trigger an immune response. The vaccines for Zika are still being explored, but recombinant adenovirus vector-based vaccines under study resemble that used in Covid-19 vaccines.
Current Status of Zika Vaccines

Some of the vaccine candidates tested have reached clinical trial and some of them have had some measure of efficacy. The most advanced candidates include:
a. mRNA-1325 (Moderna): This type of vaccine is developed using the messenger RNA that has already passed through safety and efficacy trials in its first phase.
b. ZPIV (Walter Reed Army Institute of Research): An inactivated virus vaccine that has shown promising results in trials for immunity building.
c. TV003 (National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases): A live attenuated vaccine that has shown promising results in early-phase trials, with ongoing studies to assess its safety in pregnant women.
Therapeutic Approaches
Antiviral Therapies
While there are no specific antiviral drugs approved for Zika virus, several compounds are being investigated:
Favipiravir: An antiviral compound with the capacity to inhibit the Zika virus in tissue culture and in vivo experiments. Before it can be recommended for use in the management of such conditions in humans, clinical trials are required to be conducted.
Chloroquine: Despite the fact that chloroquine has been used as an antimalarial drug it has shown some effectivity against Zika virus when tested in vitro. Yet it has yet still to fulfill clinical potential.
Ribavirin: In addition, there is another antiviral drug that have been found to have activity against Zika virus, however, those drugs have many side effects, and low efficacy rating has made people to stop using these drugs.
Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) represent a promising therapeutic approach for Zika virus:
ZKA190: A human mAb that has demonstrated high and broad-spectrum neutralizing capability against the Zika virus in vitro. Due to current trail findings it is certified to be safe and it is also being trailed to determine its efficiency.
ZIKV-117: The other mAb that has shown efficiency in preventing complex and the Zika virus in animal models. In humans, more research is required in order to delineate its uses.
Host-Targeted Therapies
Researchers are also exploring host-targeted therapies that modulate the host's immune response to Zika virus:
Interferons: These proteins are essential to the human body’s viral immunity. Research is being conducted to show how Interferons that help in enhancing the immune response to the virus can be applied in fighting the Zika virus.
Immunomodulators: Biological regulators that straddle the immune system are considered for their efficacy to boost the body’s viral resistance and lessen viral infections and their ramifications.
Challenges and Future Directions
Safety Concerns
Keeping the vaccines and treatments safe for pregnant women and the babies being carried by these women is still a major issue. Regarding adverse effects and risks the use of probiotics necessitates extensive investigations.
Long-Term Immunity
There is a need to assess the length of the immunity that is offered by the vaccine since it is one of the most vital factors to look into. Further studies are being carried out to evaluate the durability of immune reactions and the use of revaccination.
Global Access
To prevent the emergence of the new Zika virus strains, health care workers need equal accommodation in terms of vaccines and other treatments, especially where the surrounding country has a limited economy. More endeavors should be made in order to provide the requisite and effective interventions to the endangered groups in the whole world.
Emerging Variants
Similar to other viruses, the appearance of new mutations of Zika virus could potentially affect the vaccine and the treatments’ efficacy. In order to adjust such actions accordingly, constant monitoring and research has to be conducted.
Conclusion:
Maintaining adequate resources and applying these innovative techniques will help in eradicating the zika virus, because vaccines and treatments for zika virus are currently under development and there are few candidates that are undergoing trials. However, there are some drawbacks, the recent development in vaccines and therapeutic strategies can be used in the enhancement of the prevention and control of Zika virus infections. Further research, partnership and investment are still required to implement such solutions and save endangered groups.